Toll Free No.: 1800 2330 0007 email: admin@dhanwantari.com

First Aid
First Aid & Emergency Treatment Guide
First Aid is the temporary help given to an injured or a sick person before professional medical treatment can be provided. This timely assistance, comprising of simple medical techniques, is most critical to the victims and is, often, life saving. Any layperson can be trained to administer first aid, which can be carried out using minimal equipments. Basic training in first aid skills should be taught in school, in work places and, in general, be learnt by all, as it is mandatory to our modern and stressful life.
ACNE
What is ACNE ?
| 1. | It is a group of skin rashes | |
| 2. | Acne Vulgaris, popularly called pimples, affects face | |
| 3. | Caused by blocked hair follicles | |
| 4. | Commonly affects the young |
Causes
| 1. | Increase in sex hormones during puberty | |
| 2. | Oil glands of skin produce more secretions | |
| 3. | Dead cells and secretions block hair follicles causing infections | |
| 4. | Infected follicles gets inflamed leading to acne |
Factors that can worsen your Acne
| 1. | Hormonal changes during menses. | |
| 2. | Squeezing of pimples | |
| 3. | Pollution and high humidity | |
| 4. | Oily diet |
Myths associated with the cause of Acne
| 1. | Chocolates, junk food, dirty skin, and stress cause acne | |
| 2. | No scientific backing for these myths |
Treatment
| 1. | Consult a skin specialist or dermatologist | |
| 2. | Common medications include -
 Benzoyl peroxide Benzoyl peroxide Resorcinol Resorcinol Salicylic acid Salicylic acid Sulfur drugs Sulfur drugs |
Skin Care
| 1. | Clean skin with mild Cleanser | |
| 2. | Avoid squeezing of pimples | |
| 3. | Avoid sunburn | |
| 4. | Use oil-free cosmetics | |
| 5. | Avoid fizzy drinks | |
| 6. | Eat a balanced diet | |
| 7. | Drink plenty of fluids |
Anaphylaxis
What is Anaphylaxis?
| 1. | Severe, life- threatening allergic reaction | |
| 2. | Occurs as a reaction to an allergen | |
| 3. | Anaphylaxis releases various chemicals in body | |
| 4. | Reactions occur in secs / mins of exposure | |
| 5. | Occurs in 30 per 100,000 individuals per year |
Causes
| 1. | Food like nuts, milk, eggs, fish | |
| 2. | Insect sting | |
| 3. | Latex | |
| 4. | Vaccines | |
| 5. | Medications like antibiotics, anesthetics | |
| 6. | Medications like antibiotics, anesthetics | |
| 7. | Medications like antibiotics, anesthetics |
What happens ?
| 1. | On first exposure-allergen specific antibody, Ig-E, produced | |
| 2. | On re-exposure, Ig-E triggers immune response | |
| 3. | This immune response is anaphylaxis |
Symptoms
| 1. | Tingling / warm sensation | |
| 2. | Itchiness / Rash | |
| 3. | Swelling of areas around mouth / throat | |
| 4. | Restricted air-ways | |
| 5. | Reduced oxygen level in brain | |
| 6. | Signs of asthma | |
| 7. | Vomiting | |
| 8. | Cramps | |
| 9. | Diarrhea | |
| 10. | Fluid–filled lungs | |
| 11. | Low blood pressure | |
| 12. | Palpitations / feeling faint | |
| 13. | Loss of consciousness |
Who is at risk?
| 1. | Those with history of food allergy | |
| 2. | Those with family history of allergies | |
| 3. | Those who have experienced prior attack |
Treatment
| 1. | If nauseated, lie down on the side | |
| 2. | If feeling faint, lie down, legs raised | |
| 3. | In case of breathing difficulty, sit up | |
| 4. | First time patients should be hospital treated | |
| 5. | Epinephrine injections – effective treatment | |
| 6. | Continuous monitoring mandatory | |
| 7. | Severity/ response / prior episodes determine treatment |
Prevention
| 1. | Avoid allergens as far as possible | |
| 2. | Those at risk should carry adrenalin auto-injector | |
| 3. | Inform school authorities, if children at risk | |
| 4. | Children should wear food allergy badges | |
| 5. | Emergency protocols necessary in schools/ work place | |
| 6. | Educating the public is vital |
Animal Bites
Overview
| 1. | Domestic pets cause more bites | |
| 2. | Dogs more likely to bite, cats more infectious | |
| 3. | Risk of rabies with non-immunized pets / wild animals |
Symptoms
| 1. | Skin break | |
| 2. | Bruise / puncture | |
| 3. | Cuts | |
| 4. | Bleeding | |
| 5. | Swelling and redness of the area | |
| 6. | Oozing of fluid |
Treatment
| 1. | Calm the affected person | |
| 2. | Wash hands before attending to wound | |
| 3. | Wash wound with soap & running water | |
| 4. | Apply antibiotic ointment | |
| 5. | Dress using sterile bandage | |
| 6. | After first aid, medical treatment must be sought quickly | |
| 7. | Suturing may be required | |
| 8. | Tetanus booster / antibiotics required | |
| 9. | Treatment depends on type / location of wound |
Prevention
| 1. | Avoid keeping wild animals as pets | |
| 2. | Choose a pet that is friendly to children | |
| 3. | Train the pet to obey commands | |
| 4. | Vaccinate your pet | |
| 5. | When children are around, pets supervision is required | |
| 6. | Avoid leaving infants alone with pets |
Asthma
Overview
| 1. | It is a chronic lung disease | |
| 2. | It creates narrowing of air passages of the lung | |
| 3. | Produces difficulty in breathing. |
Symptoms
| 1. | Wheezing | |
| 2. | Cough and cold | |
| 3. | Tightness in the chest | |
| 4. | Sticky mucus | |
| 5. | Disturbed sleep | |
| 6. | Breathlessness |
Causes
| 1. | Hereditary factors | |
| 2. | Environmental factors like dust, mite, pollen | |
| 3. | Occupational exposure to irritants | |
| 4. | Dietary Changes | |
| 5. | Lack of exercise |

Asthma Triggering Factors
| 1. | Colds and viruses | |
| 2. | Irritants like Cigarette smoke, scent, pollution | |
| 3. | Cold air or change in weather | |
| 4. | Physical exertion | |
| 5. | Allergens like dust, mite, pollen, furs | |
| 6. | Some medications | |
| 7. | Infections | |
| 8. | Stress |
Myths about asthma
| 1. | It is contagious | |
| 2. | It cannot be controlled | |
| 3. | Asthma medicines are addictive |
Management of Asthma
| 1. | Asthma cannot be cured, but it can be controlled | |
| 2. | Keep the house clean | |
| 3. | Use hardwood floors or tile | |
| 4. | Avoid carpets in house | |
| 5. | Avoid pets with fur or feathers | |
| 6. | Use clean bed sheets & pillow covers | |
| 7. | Use bed made of synthetic materials | |
| 8. | Use air conditioner | |
| 9. | Maintain low humidity at home |
Treatment
| 1. | Anti-inflammatory drugs include:
 Steroid Inhalers Steroid Inhalers Sodium Chromoglycate Sodium Chromoglycate
|
|
| 2. | Treatment –Bronchodilators | |
| 3. | Common bronchodilators include:
 Salbutamol Inhalers Salbutamol Inhalers Terbutaline Tabs Terbutaline Tabs
|
|
| 4. | Consult your Pulmonologist |
Famous sports person with asthma
| 1. | Ian Botham (Cricketer) | |
| 2. | Jackie Joyner Kersee (Athlete) | |
| 3. | Mark Spitz (Swimmer) |
Back pain
What is Back Pain ?
| 1. | Short-term, acute pain in the back | |
| 2. | Indicates that body is under stress |
Causes
| 1. | Bones and ligaments of spine | |
| 2. | Muscles and nerves of the Back |
Back pain triggered by
| 1. | Poor posture | |
| 2. | Inappropriate footwear | |
| 3. | Incorrect walking habits | |
| 4. | Strained muscles | |
| 5. | Prolonged sitting | |
| 6. | Sleeping on soft mattresses | |
| 7. | Kidney, bladder, or prostate disorders | |
| 8. | Pregnancy | |
| 9. | Constipation | |
| 10. | Stress |
Back pain triggered by
| 1. | Rest in a comfortable position | |
| 2. | Apply ice pack to affected area | |
| 3. | Painkillers or relaxants may be used | |
| 4. | Avoid strenuous exercise | |
| 5. | Avoid pillows | |
| 6. | Avoid sleeping on soft mattress |
Treatment
| 1. | Anti-inflammatory drugs | |
| 2. | Massage with hot/ cold packs | |
| 3. | Massage with hot/ cold packs | |
| 4. | Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulator(TENS) | |
| 5. | Regular simple exercises | |
| 6. | Consult an Orthopedician if:
 Pain persists Pain persists Difficulty in passing urine Difficulty in passing urine Numbness or pain in legs or toes Numbness or pain in legs or toes |
Prevention
| 1. | Maintain good posture | |
| 2. | Do not smoke | |
| 3. | Avoid overstretching body | |
| 4. | Reduce stress/ strain | |
| 5. | Take breaks during work | |
| 6. | Sit straight with lower back support | |
| 7. | Use comfortable low-heeled shoes | |
| 8. | Do stretching exercises |
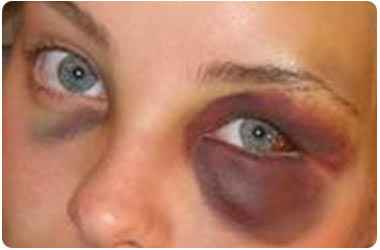
Black Eye
What is Black eye?
| 1. | A bruise in the tissues around the eye/eyes | |
| 2. | Results from injury to face/head | |
| 3. | Causes swelling and dark coloration of eye | |
| 4. | Hence, "black eye" | |
| 5. | Usually a minor problem | |
| 6. | Sometimes it indicates a serious injury | |
| 7. | One or both eye affected |
Causes
| 1. | Blow to eye / nose | /|
| 2. | Facial surgical procedures | |
| 3. | Allergies | |
| 4. | Bites |
Symptoms
| 1. | Discoloration of eye | |
| 2. | Swelling | |
| 3. | Blow to nose causes swelling of eye | |
| 4. | Head injuries may blacken/swell eyes | |
| 5. | Pain | |
| 6. | Blurry vision due to swelling | |
| 7. | Headache |
Symptoms of severity
| 1. | Persistent headache | |
| 2. | Double vision | |
| 3. | Inability to move eye/eyes | |
| 4. | Blood on eye surface | |
| 5. | Blood/fluid issue from nose, ears | |
| 6. | Loss of consciousness | |
| 7. | Loss of sight |
Treatment
| 1. | Black eyes generally heals within a few days | |
| 2. | Consult with specialist for serious injuries |
Home remedy
| 1. | Apply ice for 20 min/hour, first two days | |
| 2. | If not better, apply warm compress once in two hours | |
| 3. | Do not use ice directly | |
| 4. | Wrap ice in cloth or use commercial pack | |
| 5. | Continue cold compress till severity eases | |
| 6. | Take acetaminophen, for pain relief | |
| 7. | Avoid aspirins / non-steroidal medications | |
| 8. | These medications may cause bleeding | |
| 9. | Stay away from strenuous activity | |
| 10. | See a medical specialist as soon as possible |
Treatment for complications
| 1. | For head injuries-Neurosurgeon | |
| 2. | For nose injuries-ENT specialist | |
| 3. | For eye injuries-Ophthalmologist | |
| 4. | For face | |
| 5. | Injuries/disfigurement-Plastic surgeon | |
| 6. | Carry out follow-up as advised by doctor |
Prevention
| 1. | Protect your eyes always | |
| 2. | Ensure safety at home by removing unwanted objects | |
| 3. | Avoid fist fights |
Bleeding Gums
Overview
| 1. | Progressive disease affecting oral cavity | |
| 2. | Characterized by chronic bleeding of gums | |
| 3. | May lead to tooth loss |
Causes
| 1. | Poor oral hygiene | |
| 2. | Inadequate plaque removal | |
| 3. | Oral trauma, like toothbrush abrasion | |
| 4. | Inflammation caused by infection | |
| 5. | Vitamin C / K deficiency | |
| 6. | Hot food | |
| 7. | Chemical irritants | |
| 8. | Leukemia | |
| 9. | Pregnancy |

Treatment
| 1. | Apply pressure using ice-pack | |
| 2. | Mouth rinse: Pinch of salt in lukewarm water | |
| 3. | Rinse twice a day to reduce swelling | |
| 4. | Consult a dentist if bleeding continues | |
| 5. | Avoid aspirin intake | |
| 6. | Massage gums regularly | |
| 7. | Reline poorly fitted dentures | |
| 8. | Take vitamin supplements if necessary |
Prevention
| 1. | Avoid Tobacco | |
| 2. | Avoid snacking between meals | |
| 3. | Reduce Carbohydrate- rich food | |
| 4. | Remove plaque every 6 months | |
| 5. | Brush teeth using soft-bristled brush | |
| 6. | Floss teeth regularly |
Blisters
What are Blisters?
| 1. | Occurs due to friction caused by constant rubbing of shoes / clothes | |
| 2. | Outer skin layer separates from inner layer | |
| 3. | The space in-between fills up with fluid | |
| 4. | Common in athletes, trekkers, rowers | |
| 5. | Also seen in people using new shoes |
Fever Blisters
| 1. | Fever blisters appear in /around mouth | |
| 2. | Fever blisters caused by virus, Herpes Simplex | |
| 3. | Type-1 Herpes virus usually involved in fever blisters | |
| 4. | These blisters are contagious | |
| 5. | Recurrent episodes may occur | |
| 6. | Recurrence due to stress/illness/injury/sunlight |
Symptoms
| 1. | Bubble-like structures on skin | |
| 2. | Redness over the area | |
| 3. | Itching | |
| 4. | Pain |
Treatment
| 1. | Make a hole at the edge of blister | |
| 2. | Use a sterilized needle or pin | |
| 3. | Pin/needle sterilized by passing over flame | |
| 4. | Drain the accumulated fluid | |
| 5. | Keep skin intact to prevent infection | |
| 6. | Clean blister with gauze containing iodine/alcohol | |
| 7. | Apply antibiotic ointment | |
| 8. | Cover with adhesive bandage for small blister | |
| 9. | Use porous, bandage for large ones | |
| 10. | Do not puncture blister if painless | |
| 11. | Do not puncture a blood-filled blister | |
| 12. | Blisters disappear in a few days time | |
| 13. | Diabetics should consult doctor |
Managing for fever (Oral) blisters
| 1. | No permanent cure/vaccination for Herpes infection | |
| 2. | Keep blisters dry & free of infection | |
| 3. | Eat a bland diet |
Prevention
| 1. | Wear the right size shoe | |
| 2. | Cover the potential area with taping | |
| 3. | Keep feet dry always | |
| 4. | Avoid touching blisters | |
| 5. | Avoid contact with an infected person | |
| 6. | Avoid stressful situations |
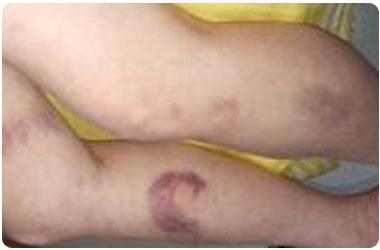
Bruises (Hematoma)
Overview
| 1. | Bruises are injuries to the soft tissue | |
| 2. | It is an 'area of discoloration' on the skin | |
| 3. | Other names - Hematoma, Contusion | |
| 4. | Can last for days to several months |
Causes
| 1. | Sports Injuries | |
| 2. | Accidents | |
| 3. | Falls | |
| 4. | Blows from objects/people | |
| 5. | Chances increase if taking medications, like Aspirin |
Types
| 1. | Subcutaneous-underneath the skin | |
| 2. | Intramuscular - within the underlying muscles | |
| 3. | Periosteal-bruise related to bone |
Related events
| 1. | Small veins and capillaries under the skin breaks | |
| 2. | Blood escapes and collects under skin | |
| 3. | In the beginning bruises look purplish or red | |
| 4. | In 2 days it may change to black or blue color | |
| 5. | It changes to a green/yellow color in 5 days | |
| 6. | Changes to a brown shade in 10-14 days | |
| 7. | It further lightens and fades away | |
| 8. | The changing colors indicates red cell metabolism |
Symptoms
| 1. | Pain | |
| 2. | Swelling | |
| 3. | Discoloration |
Treatment
| 1. | Most bruises vanish in 2 weeks time | |
| 2. | No bandage required if skin is not broken | |
| 3. | Keep bruised area raised | |
| 4. | Apply cold compress, ½ hr to one hr at a time | |
| 5. | Continue this for two days | |
| 6. | Avoid draining the bruise using needle | |
| 7. | Do not apply ice directly on skin | |
| 8. | Can take pain killing medications, like acetaminophen | |
| 9. | Avoid using the bruised part | |
| 10. | For more serious injury consult a doctor | |
| 11. | Consult also in case of spontaneous injury/infection | |
| 12. | Protein-bioflavinoids-Vit C rich food helps healing |
Treatment
| 1. | Teach children safety measures | |
| 2. | Avoid falls around house | |
| 3. | Wear seat belts while driving | |
| 4. | Wear helmet while riding | |
| 5. | While sporting, pad frequently- bruised areas |
Burns
What are burns?
| 1. | Injuries due to heat/ chemicals/ electricity/ radiation | |
| 2. | Common heat injuries due to fire, hot liquids, steam | |
| 3. | Burns due to heat / chemicals - through skin contact | |
| 4. | Severe burns affect muscles, fat and bones | |
| 5. | Older people/ children - particularly vulnerable |
Categories of burns
| 1. | First, second and third degree | |
| 2. | Categorization depends on severity of tissue damage | |
| 3. | Check extent of burn before deciding self treatment | |
| 4. | Seek help if burn is over a couple of inches in diameter | |
| 5. | If it involves large sections of the hands, feet, face, groin or buttocks, or a major joint |
First-degree burns
| 1. | Injuries are superficial / mild | |
| 2. | Swelling& redness of the injured area | |
| 3. | Pain develops | |
| 4. | No blisters seen | |
| 5. | Burned area becomes white on touch | |
| 6. | Takes 3-6 days to heal |
Treatment
| 1. | Remove patient from heat source | |
| 2. | Remove the burnt clothing | |
| 3. | Run cool water over burnt area | |
| 4. | Gently clean the injured area | |
| 5. | Gently dry | |
| 6. | Apply anti biotic such as Silver Sulphadiazine | |
| 7. | Use a sterile bandage to cover burns | |
| 8. | Take tetanus vaccination, if required |
Second-degree burns
| 1. | Burns extends to middle skin layer, dermis | |
| 2. | Swelling, redness and pain observed | |
| 3. | Burnt area may turn white on touch | |
| 4. | Blisters develop, that ooze a clear fluid | |
| 5. | Scars may develop | |
| 6. | Restricts movement, if injury occurs at joint | |
| 7. | Dehydration may occur | |
| 8. | Healing time varies, depends on extent of injury |
Treatment
| 1. | Clean the affected area thoroughly | |
| 2. | Gently dry | |
| 3. | Apply antibiotic cream over affected area | |
| 4. | Make the patient lie down | |
| 5. | Keep burnt body part at a raised level | |
| 6. | Skin graft may be required | |
| 7. | Physical therapy may be essential to aid mobility | |
| 8. | Splints may be used to rest affected joints | |
| 9. | Hospitalization is essential |
Third-degree burns
| 1. | Damage occurs to all 3 skin layers | |
| 2. | Destroys adjacent hair follicles, sweat glands, nerve endings | |
| 3. | Lack of pain due to destroyed nerves | |
| 4. | Injured area does not turn white on touch | |
| 5. | No blisters observed | |
| 6. | Swelling occurs | |
| 7. | Skin develops leathery texture | |
| 8. | Discoloration of skin observed | |
| 9. | Scars develop | |
| 10. | Crusty surfaces (Eschars) develop-impairs circulation | |
| 11. | Dehydration occurs resulting in shock | |
| 12. | Symptoms may worsen with time | |
| 13. | Disfigurement may result | |
| 14. | Healing depends on extent of injury | |
| 15. | 90% body surface injury results in death | |
| 16. | 60% injury in elderly, fatal |
Treatment
| 1. | Requires immediate hospital care | |
| 2. | Dehydration treated through intravenous fluid supply | |
| 3. | Oxygen is administered | |
| 4. | Eschars are surgically opened | |
| 5. | Periodically run clean cool water over burns | |
| 6. | Nutritious diet helps to heal quickly | |
| 7. | Regular monitoring essential | |
| 8. | Mental Depression treated by anti-depressants |
Prevention
| 1. | Install smoke alarm in your home | |
| 2. | Employ 'children friendly' safety measures at home | |
| 3. | Avoid synthetic clothing while cooking | |
| 4. | Carry out fire drills at home and work place |
Cardio-pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
About Cardiac Arrest
| 1. | Often caused by abnormal heart rhythm | |
| 2. | This aberrant rhythm is ventricular fibrillation (VF) | |
| 3. | During VF heart stops pumping blood | |
| 4. | Patient may stop breathing | |
| 5. | No pulse may be detected | |
| 6. | A shock to the heart, called defibrillation, required | |
| 7. | Defibrillation stops VF, restores heart function |
What is CPR?
| 1. | Emergency life-saving measure | |
| 2. | Combination of rescue breathing & chest compressions | |
| 3. | Done on unconscious/ non-breathing patient | |
| 4. | Done on persons suffering cardiac arrest | |
| 5. | Also for near-drowning/ asphyxiation/ trauma cases | |
| 6. | CPR conducts defibrillation | |
| 7. | Supports heart pumping for short duration | |
| 8. | Allows oxygen to reach brain | |
| 9. | Buys time till help arrives | |
| 10. | More effective when done as early as possible |
The Vital Steps Clear the airway
| 1. | Assess if the person is conscious / breathing | |
| 2. | Lay the person on his back on a hard surface | |
| 3. | Using a head tilt -chin lift open his airway | |
| 4. | Check for breathing sound | |
| 5. | If not breathing, start mouth-to-mouth breathing |
Mouth- to-mouth breathing
| 1. | Pinch the person's nostril shut | |
| 2. | Seal his mouth with your own | |
| 3. | Give the first breath, lasting one second | |
| 4. | Watch if chest rises | |
| 5. | If it rises, give second rescue breath | |
| 6. | If it does not rise, give a head tilt- chin lift | |
| 7. | Now give second rescue breath |
Restore circulation through compression
| 1. | Place heel of your palm on patient's chest | |
| 2. | Place your other hand above first | |
| 3. | Keep elbows straight | |
| 4. | Push down using upper body weight (compress) | |
| 5. | Push hard and fast | |
| 6. | After 30 compressions, clear airway | |
| 7. | Give two rescue breaths | |
| 8. | This is one cycle | |
| 9. | Give 100 compressions /minute | |
| 10. | Continue CPR till medical help arrives |
CPR for children (under 8 yrs/ infant)
| 1. | Procedure almost same as for adult | |
| 2. | Following details should be incorporated | |
| 3. | 20 breaths/min should be delivered | |
| 4. | 100 compressions/minute should be given | |
| 5. | Chest compressions - given with one hand |
Prognosis
| 1. | If done well, CPR saves life | |
| 2. | Normalcy is restored in rescued person | |
| 3. | CPR can also be ineffective, causing death | |
| 4. | In some cases, causes injuries / damages |
Caution
| 1. | Ribs/heart/lungs/ liver may be injured | |
| 2. | After CPR, medical attention should be given |
CPR training
| 1. | CPR - practical skill acquired through training | |
| 2. | Professional training/ regular practice mandatory | |
| 3. | CPR not confined to medical professionals | |
| 4. | Community organizations, like Red Cross, conduct training |
Chemical Splash in the Eye
Overview
When a toxic chemical is splashed into the eye(s), it could cause serious complications that may lead to blindness.
Causes
| 1. | Working with chemicals in factories | |
| 2. | Handling car battery | |
| 3. | Working in research laboratories | |
| 4. | Handling household chemicals |
Symptoms
| 1. | Irritation in eye | |
| 2. | Eye Burns | |
| 3. | Watering of the eye |
Treatment
| 1. | Lay the person on the floor | |
| 2. | Keep eye lids open forcibly | |
| 3. | Use clean cold water to wash eyes gently | |
| 4. | Keep washing steadily for at least 20 minutes | |
| 5. | Rinse/wash hands thoroughly to remove chemical | |
| 6. | If wearing contact lens remove them | |
| 7. | Do not rub eyes | |
| 8. | Do not use eye drops until told | |
| 9. | Wear sunglasses to minimize irritation | |
| 10. | After these basic steps seek medical help | |
| 11. | Remember the name of chemical to tell doctor |
Prevention
| 1. | If working with chemicals, wear protective face-mask | |
| 2. | Wear eye goggles whenever required | |
| 3. | Do not be careless with chemicals | |
| 4. | Store household chemicals safely | |
| 5. | Keep chemicals out of reach of children |
Chest pain
Overview
Feeling of pain /discomfort between neck and abdomen
| 1. | Chest pain raises fear of heart attack | |
| 2. | Any tissue or organ in chest can cause pain | |
| 3. | 'Angina' is heart- related chest pain |
Causes
| 1. | Some mild, others life threatening | |
| 2. | Problems related to the heart | |
| 3. | Asthma | |
| 4. | Some mild, others life threatening | |
| 5. | Problems related to the heart | |
| 6. | Asthma | |
| 7. | Pneumonia | |
| 8. | Inflammation in the lung | |
| 9. | Inflammation / strain of rib muscle | |
| 10. | Anxiety | |
| 11. | Indigestion / ulcers in stomach | |
| 12. | Gall bladder stones | |
| 13. | Shingles | |
| 14. | Stress |
Symptoms
| 1. | Pain or pressure in chest area | |
| 2. | May be accompanied by
 Heartburn Heartburn Resorcinol Resorcinol Vomiting acid Vomiting acid Dizziness Dizziness Shortness of breath Shortness of breath Fever Fever |
Treatment
| 1. | If you have asthma or angina take your regular medications | |
| 2. | Medicines like acetaminophen and ibuprofen may help | |
| 3. | Consult a doctor if
 Pain /fever /cough persists Pain /fever /cough persists Radiating pain occurs Radiating pain occurs Angina occurs at rest Angina occurs at rest The cough produces yellow -green phlegm The cough produces yellow -green phlegm Pressure / tightness occurs Pressure / tightness occurs Nausea Nausea  Dizziness Dizziness Shortness of breath Shortness of breath Sweating Sweating |
|
| 4. | Hospitalization may be essential | |
| 5. | Tests like ECG, may have to be taken |
Prevention
| 1. | Maintain normal weight | |
| 2. | Exercise regularly for 30 - 40 minutes | |
| 3. | Check and control BP, diabetes, cholesterol | |
| 4. | Avoid smoking | |
| 5. | Eat low fat balanced diet | |
| 6. | Get health check ups done regularly | |
| 7. | Control stress |
Chicken pox
What is Chicken Pox?
| 1. | Common childhood disease | |
| 2. | Infection mild in children | |
| 3. | Serious in infants/ adults | |
| 4. | Chances of recurrence present | |
| 5. | World-wide incidence |
Causes
| 1. | Caused by virus, Varicella-Zoster | |
| 2. | Spreads through air & contact | |
| 3. | Contagious till blisters disappear |
Symptoms
| 1. | Rashes all over body | |
| 2. | Fever | |
| 3. | Blisters | |
| 4. | Uncontrollable itching | |
| 5. | Pneumonia | |
| 6. | Brain damage in severe cases |
Treatment
| 1. | Take luke-warm baths | |
| 2. | Avoid aspirin | |
| 3. | Trim fingernails to avoid skin damage | |
| 4. | Drink cold fluids | |
| 5. | Acyclovir effectively treats chicken pox | |
| 6. | Fever treated with Acetaminophen/ibuprofen | |
| 6. | Consult a GP /child specialist if:
 Rashes involve eyes Rashes involve eyes Fever is 103 °F or more Fever is 103 °F or more Infection persists Infection persists |
Prevention
| 1. | Infected person should remain home-bound | ||||||||||
| 2. | Vaccination | ||||||||||
| 3. | First dose given between 12-18 months | ||||||||||
| 4. | Vaccination should not be given to:
|
Choking
Overview
| 1. | Occurs when foreign object is lodged in windpipe | |
| 2. | This blocks oxygen supply to brain | |
| 3. | In adults, choking occurs due to food | |
| 4. | In children it also occurs on swallowing an object |
Causes
| 1. | Swallowing a large piece of food | |
| 2. | Swallowing food that is not well chewed | |
| 3. | Eating food quickly | |
| 4. | Eating and talking | |
| 5. | Consuming alcohol before a meal | |
| 6. | Wearing dentures | |
| 7. | Being careless about children | |
| 8. | Walking / playing with food in mouth |
Symptoms
| 1. | Hands will grasp throat | |
| 2. | Breathlessness | |
| 3. | Noisy breathing | |
| 4. | Inability to cough | |
| 5. | Skin, nails and lips may turn blue | |
| 6. | Loss of consciousness |
Treatment
| 1. | Heimlich maneuver and CPR –2 techniques | |
| 2. | If person is unable to talk, try Heimlich maneuver | |
| 3. | Forces the diaphragm upto the lungs | |
| 4. | Creates an artificial cough |
Heimlich Maneuver on a standing person
| 1. | Stand behind the person | |
| 2. | Form a fist with one hand | |
| 3. | Place fist below ribcage, thumb inward | |
| 4. | Hold the fist with other hand | |
| 5. | Keep arms off ribcage | |
| 6. | Give four inward and upward thrust | |
| 7. | Repeat till the object is ejected | |
| 8. | Same method is used for a child too |
Heimlich Maneuver On an Unconscious Person
| 1. | If person is lying down, straddle the person with your knees | |
| 2. | Place heel of one hand above waistline | |
| 3. | Place other hand over the first | |
| 4. | Give four inward and upward thrust | |
| 5. | Repeat till object is coughed out |
Heimlich Maneuver On an Infant
| 1. | Place your forearm over your raised knees | |
| 2. | Place the infant face down over your fore arm | |
| 3. | Give four blows using the heel of your hand | |
| 4. | Repeat till object comes out | |
| 5. | If it does not work, turn the baby | |
| 6. | Place two fingers an inch below the imaginary line connecting nipples | |
| 7. | Give four thrusts forcefully to bring out the object | |
| 8. | Repeat if required |
Prevention
| 1. | While eating, concentrate on the task | |
| 2. | Do not eat quickly, without chewing | |
| 3. | Supervise children while they eat | |
| 4. | Give easily chewable, soft food to children | |
| 5. | Do not leave tiny objects within the reach of children |
Corneal Abrasion
Overview
| 1. | Cornea is outer layer of the eye | |
| 2. | Tearing away of this layer leads to corneal abrasion. | |
| 3. | Most common injury to the eye | |
| 4. | Multiple nerve endings present in cornea, hence painful |
Causes
| 1. | A finger nail | |
| 2. | Any sharp flying object like pencil, glass | |
| 3. | Tiny particles, like sand | |
| 4. | Contact lens |
Symptoms
| 1. | Pain | |
| 2. | Redness of the eye | |
| 3. | Blurred vision | |
| 4. | Discomfort in the eye | |
| 5. | Difficulty in opening eyes | |
| 6. | Head ache | |
| 7. | Discharge of tears |
Treatment
| 1. | Antibiotic used to prevent infection | |
| 2. | Examination is done after using an anaesthetic | |
| 3. | Pain returns after anaesthetic is stopped | |
| 4. | Repeated usage of anaesthetic is harmful | |
| 5. | Eye ointments, pain relievers are provided | |
| 6. | A ‘patch’ may be put on the eyes | |
| 7. | Eye ointments/ lubricants at night prevents recurrence |
Do Not
| 1. | Do not rub eyes during healing phase | |
| 2. | This may destroy the newly forming cells | |
| 3. | Repatching may then be necessary | |
| 4. | Do not wear contact lens till cured |
Prognosis
| 1. | Small corneal abrasions heal quickly | |
| 2. | Blurriness may last for a few weeks | |
| 3. | Permanent loss of sight is rare | |
| 4. | Occasionally abrasions may recur |
Prevention
| 1. | Always follow instructions while using contact lens | |
| 2. | Do not wear contact lens for too long | |
| 3. | Remove lens if irritation /dryness occurs | |
| 4. | Do not rub eyes too hard | |
| 5. | Wash hands whenever required | |
| 6. | Trim your nails regularly | |
| 7. | Be careful while using ‘glitter’ make up | |
| 8. | Wear protective gears while sporting |
Cuts
What is Cut?
An injury due to opening in the skin
Minor Cuts / Scrapings
| 1. | No treatment is required | |
| 2. | Care required to prevent infection |
Treatment for Minor Cuts
| 1. | Clean wound with water | |
| 2. | Avoid soap | |
| 3. | Remove dirt/debris in the wound | |
| 4. | Apply antibiotic ointment | |
| 5. | Dress/ bandage the wound | |
| 6. | Change dressing daily | |
| 7. | Minor cuts stop bleeding in10 min | |
| 8. | Apply gentle pressure if bleeding persists |
Deep cuts
| 1. | May bleed heavily | |
| 2. | May expose underlying tissues |
Treatment For Deep Cuts
| 1. | May require stitching | |
| 2. | Requires Tetanus Toxoid (TT) if:
 Cut is dirty or has debris Cut is dirty or has debris TT taken 5 years ago TT taken 5 years ago |
|
| 3. | Consult a doctor in case of:
 Delayed wound- healing Delayed wound- healing Pus Discharge Pus Discharge Fever Fever |
Points to note
| 1. | Do not try to clean a major wound | |
| 2. | Do not remove deeply- lodged debris | |
| 3. | Do not breathe on an open wound | |
| 4. | Do not push back exposed body parts |
Dandruff
What is Dandruff?
| 1. | White flakes of dead skin | |
| 2. | Dandruff mostly affects scalp | |
| 3. | Not a health hazard but a nuisance |
Symptoms
| 1. | Itchy, scaly scalp |
Causes
| 1. | A fungus, Malassezia | |
| 2. | It feeds on scalp's natural oils | |
| 3. | Produces acid which causes itch | |
| 4. | Other factors-
 Climate Climate Stress Stress Hormone production Hormone production Oily skin Oily skin Food habits Food habits |
Treatment
| 1. | Use anti-dandruff, conditioner-based shampoo | |
| 2. | Rinse scalp for 5 minutes with shampoo | |
| 3. | If resistant, apply 1 % hydrocortisone cream | |
| 4. | If severe, consult a dermatologist /trichologist |
Prevention
| 1. | Cannot be prevented but managed | |
| 2. | Use good quality shampoo | |
| 3. | Wash hair frequently | |
| 4. | Avoid using gels/ waxes | |
| 5. | Eat a healthy diet |
Related infections
| 1. | Psoriasis, Impetigo, Tinea capitis |
Diabetes
What is Diabetes?
| 1. | Chronic health condition | |
| 2. | Insufficient insulin produced /used | |
| 3. | Affects sugar breakdown |
Introduction
| 1. | Food eaten converted to glucose | |
| 2. | Glucose produces energy | |
| 3. | Insulin breaks down glucose | |
| 4. | Diabetics do not sufficiently produce or use insulin | |
| 5. | Causes blood sugar build-up in blood |
Types
A. Type I diabetes
 Mostly occurs in children/young adult Mostly occurs in children/young adult  Insulin production affected Insulin production affected |
B. Type II diabetes
 Mostly occur in adults Mostly occur in adults Body is partially/ fully insulin resistant Body is partially/ fully insulin resistant Blood sugar level increases Blood sugar level increases |
C. Gestational diabetes
 Occurs in pregnant women Occurs in pregnant women  Causes problems in mother and baby Causes problems in mother and baby |
Symptoms
| 1. | Increased thirst | |
| 2. | Excessive urination | |
| 3. | Weight loss | |
| 4. | Weakness | |
| 5. | Vision changes | |
| 6. | Dry skin / dehydration | |
| 7. | Numbness in hands/ feet |
Diagnosis
| 1. | Fasting blood glucose level> 126 mg/dL | |
| 2. | Random Blood Glucose> 200 mg/dL |
Complications of diabetes
| 1. | Diabetic Retinopathy (eye) | |
| 2. | Kidney Disease | |
| 3. | Heart Disease and Stroke | |
| 4. | Nerve Disease | |
| 5. | Impotence (sexual disorder) |
Treatment
A. Type I diabetes
| 1. | Daily Insulin injections | |
| 2. | Insulin cannot be taken as a pill |
B. Type II diabetes
| 1. | Healthy diet and exercise brings down glucose level. | |
| 2. | Some people need diabetic medicine or insulin |
C. Medications lower blood glucose level
| 1. | Sulfonylurea drugs & Meglitinedes: Produces insulin in the pancreas | |
| 2. | Biguanides: decreases glucose in liver | |
| 3. | µ- glucosidase inhibitors: Slows the absorption of starch | |
| 4. | Consult a diabetologist or general physician |
Dislocation
About Dislocation
| 1. | An injury which forces bones out of their sockets | |
| 2. | Dislocation is a common sports injury | |
| 3. | It temporarily deforms or immobilizes the joint |
Causes
| 1. | Usually caused by a trauma like a fall/blow | |
| 2. | Rheumatoid arthritis also causes dislocation |
Symptoms
| 1. | Pain | |
| 2. | Tenderness | |
| 3. | Difficulty to move injured part | |
| 4. | Swelling | |
| 5 | Discoloration |
Treatment
| 1. | Call medical help as soon as possible | |
| 2. | Do not move the joint or try to place it back | |
| 3. | Place ice to control swelling | |
| 4. | If skin is cut, clean gently and bandage with sterile gauze | |
| 5 | Sling or splint the injury in its original position | |
| 6. | If injury is serious, check for breathing | |
| 7. | If not breathing, provide Cardio pulmonary esuscitation (CPR) Elevate the feet up to 12 inches | |
| 8 | Cover the patient with a blanket |
Prevention
| 1. | Wear protective gear while sporting | |
| 2. | Make home environment safe | |
| 3. | Teach safe habits to children | |
| 4. | Do not stand on chairs or other unstable objects | |
| 5 | Exercise care while using bath oils | |
| 6. | Make use of hand rails while using the stairs |
Fever
Overview
| 1. | Fever is higher-than-normal body temperature (Normal temparature-370C or 98.60F) | |
| 2. | Indicates an abnormal process in the body | |
| 3. | Fever is a symptom and not disease | |
| 4. | Also called 'pyrexia' | |
| 5 | Low fever:98.80F to 100.80F | |
| 6. | Mild to moderate:1010F to 1030F | |
| 7. | High fever:1040F and above |

Causes
| 1. | Hot weather | |
| 2. | Childhood immunization | |
| 3. | Bacterial/viral infection | |
| 4. | Spending much time in sun | |
| 5 | Allergy to medication / food |
Symptoms
| 1. | Hot flushed face | |
| 2. | Lack of interest in food | |
| 3. | Nausea | |
| 4. | Vomiting | |
| 5. | Head and body ache | |
| 6. | Constipation | |
| 7. | Diarrhea | |
| 8. | High fevermaybe associated with - Delirium Delirium Stress Stress Convulsion Convulsion |
Treatment
| 1. | Monitor temperature using a thermometer | |
| 2. | Remove the excess clothing | |
| 3. | Keep the person in a cool place | |
| 4. | Give a sponge bath in luke warm water | |
| 5 | Give plenty of fluids | |
| 6. | Give prescribed doses of acetaminophen /paracetamol | |
| 7. | Do not give aspirin to a person with fever | |
| 8. | Do not wrap the person in blankets / warm clothing | |
| 9. | Consult a Doctor in case of - Irregular breathing Irregular breathing Stiff neck Stiff neck Confusion Confusion Rashes Rashes Persistent sore throat Persistent sore throat Vomiting Vomiting Diarrhea Diarrhea Painful urination Painful urination Convulsions Convulsions |
Food Borne Illness
| 1. | Occurs by eating contaminated food | |
| 2. | Brought about by bacterial/viral/ parasitic toxins | |
| 3. | Bacteria is most common cause of food contamination | |
| 4. | Bacteria is present in most raw food | |
| 5. | Raw meat /poultry/ sea food/ eggs: increased risk | |
| 6. | Tomatoes/sprout /lettuceare also contamination-prone | |
| 7. | Contamination occurs between production and preparation | |
| 8. | Children/pregnant women/ elderlcy/immuno-deficient at greater risk |
Symptoms
| 1. | Resembles intestinal flu | |
| 2. | Lasts for few days or weeks |
Common Symptoms are
 Nausea Nausea Abdominal cramps Abdominal cramps vomiting vomiting Diarrhea, which may be bloody Diarrhea, which may be bloody Fever Fever Dehydration Dehydration |
Common Symptoms are
 Shallow breath Shallow breath Rapid pulse Rapid pulse Pale skin Pale skin Chills Chills Chest pain Chest pain Dehydration Dehydration |
Severity may lead to hemolytic uremic syndrome, in children
Deaths may occur due to severe complications
Treatment
| 1. | Most cases are mild and are treated by taking fluids | |
| 2. | Fluids may be taken orally or intravenously | |
| 3. | Severe cases must be hospitalized |
Prevention
| 1. | Wash hands well before preparing food | |
| 2. | Clean surfaces and kitchen counters before cooking | |
| 3. | Cook food at appropriate temperatures enough to kill bacteria | |
| 3. | Refrigerate food within two hours of cooking |
Allow enough space in fridge for cool air circulation
Foreign Object In The Ear
Overview
| 1. | Any outside object lodged inside ear canal | |
| 2. | Not dislodged easily | |
| 3. | An 'Otoscope' is used to identify object |
Causes
| 1. | On purpose, eg, a cotton swab used for cleaning | |
| 2. | Accidental, especially among children | |
| 3. | An insect that may have crept into the ear |
Symptoms
| 1. | Feeling of uneasiness/ discomfort | |
| 2. | Pain | |
| 3. | Dizziness | |
| 4. | Infection | |
| 5. | Discharge/blood oozing from ear | |
| 6. | Dry cough, occasionally | |
| 7. | Insect may bite/cause tickling sensation |
Treatment
| 1. | If object is protruding, use tweezers to remove | |
| 2. | If object is small, shake head with ear facing downward | |
| 3. | If it is insect, turn head to place affected ear upward | |
| 4. | Place few drops of mineral oil/baby oil inside ear | |
| 5. | Flush the insect out using clean water | |
| 6. | Use oil only in case of insect | |
| 7. | Otherwise it may lead to swelling | |
| 8. | Seek medical help if required |
Steps to Avoid
| 1. | Do not push your finger into the ear | |
| 2. | Do not strike the head to dislodge object | |
| 3. | Do not shake a child to remove object | |
| 4. | Do not try to remove object on your own | |
| 5. | Do not block any discharge from ear | |
| 6. | Do not try to clean the ears |
Consult a doctor
| 1. | If the object is not soft | |
| 2. | If the object cannot be removed easily |
Prognosis
| 1. | There may be no problems once object is removed | |
| 2. | Trying to remove object may tear the ear drum | |
| 3. | This may lead to hearing loss |
Prevention
| 1. | Avoid using objects like tissues/ tooth pick to clean ears | |
| 2. | Do not place anything inside ear without consulting doctor | |
| 3. | Monitor children's actions |
Foreign Object In The Eye
Overview
| 1. | Any object that lodges itself in the eye | |
| 2. | Small objects will be washed out by tears / blinking | |
| 3. | Others need medical attention |
Causes
| 1. | Dust | |
| 2. | Debris | |
| 3. | Sand | |
| 4. | Contact lens | |
| 5. | Eye lash | |
| 6. | Make up | |
| 7. | Flying objects like glass |
Symptoms
| 1. | Itching | |
| 2. | Irritation | |
| 3. | Pain | |
| 4. | Sensitivity to bright light | |
| 5. | Blurry vision |
Treatment
| 1. | Wash hands before helping the victim | |
| 2. | Seat the person in a lighted area | |
| 3. | Gently examine the eye | |
| 4. | Pull lower eyelid downward | |
| 5. | Ask the person to look upward | |
| 6. | Then hold upper eyelid while person looks down | |
| 7. | If object is floating try flushing it out | |
| 8. | Otherwise, touch the object with wet cotton bud | |
| 9. | Object should cling to the cotton bud | |
| 10. | If object is removed, flush eyes with saline/warm water | |
| 11. | If object cannot be removed, see a doctor | |
| 12. | If object is embedded, do not touch | |
| 13. | Cover the eyes with paper cups and tape it | |
| 14. | Consult doctor immediately |
Steps to Avoid
| 1. | Avoid rubbing eyes | |
| 2. | Do not remove an embedded object | |
| 3. | Do not try to remove a large object |
Consult a doctor
| 1. | When the object cannot be removed | |
| 2. | When object is embedded | |
| 3. | When the person's vision is affected | |
| 4. | When the scratching sensation persists | |
| 5. | When pain persists even after removing object |
Prognosis
| 1. | Depends on type of object and mode of entry | |
| 2. | Glass/sharp objects may damage eye |
Prevention
| 1. | Wear protective eye gear at work, if necessary | |
| 2. | Wear protective gears while playing sports |
Exercise caution if using contact lens
Foreign Object In The Nose
Overview
| 1. | Any outside object inserted into nose | |
| 2. | Usually children are the affected ones | |
| 3. | During play, they insert small objects into nostrils |
Causes
| 1. | Food particles | |
| 2. | Erasers | |
| 3. | Dried seeds | |
| 4. | Objects, like crayons | |
| 5. | Beads | |
| 6. | Buttons |
Symptoms
| 1. | Irritation | |
| 2. | Infection | |
| 3. | Foul smelling / bloody discharge from nose | |
| 4. | Breathing difficulty | |
| 5. | Beads | |
| 6. | Buttons |
Treatment
| 1. | The person must be urged to breathe through mouth | |
| 2. | The person should avoid breathing with force | |
| 3. | Close the unaffected nostril | |
| 4. | Blow out gently through the affected nostril | |
| 5. | Get medical aid if this method fails |
Steps to Avoid
| 1. | Do not probe an object which is not seen | |
| 2. | Do not probe an object that is not easy to grasp | |
| 3. | Do not blow nose too hard | |
| 4. | Do not use sharp instruments to remove the object |
Consult a doctor
| 1. | When the object cannot be removed | |
| 2. | When the victim suffers from infection |
Prognosis
| 1. | No problem expected once the object is removed |
Prevention
| 1. | Children must be trained not to put objects in body openings |
Small objects must be kept out of reach of children
Foreign Object In The Skin
Overview
When object is lodged in the skin layers
| 1. | It may be embedded superficially or deeply |
Causes
| 1. | Caused by glass | |
| 2. | Wood splinters | |
| 3. | Fiber glass |
Symptoms
| 1. | Irritation | |
| 2. | Pain | |
| 3. | Abscess |
Treatment
| 1. | Wash hands well | |
| 2. | Clean the affected area using soap, water | |
| 3. | If object is visible above skin, squeeze the area around | |
| 4. | When object pops out, remove using sterile tweezer | |
| 5. | If embedded under skin, use a sterile needle | |
| 6. | Sterilize needle by flaming/wiping with alcohol | |
| 7. | Use needle to break skin over affected area | |
| 8. | Lift tip of the object | |
| 9. | Use a small tweezer to pull it out | |
| 10. | Gently squeeze the area and let bleed | |
| 11. | Clean the area with soap, water. Pat dry | |
| 12. | Apply an antibiotic |
Steps to Avoid
| 1. | Do not wet if the object is of wood | |
| 2. | Wet wooden objects swell- becomes difficult to remove |
Consult a doctor
| 1. | If the object is difficult to remove | |
| 2. | If the object is close to a sensitive body part, like the eye | |
| 3. | In case of infection |
Foreign Object When Swallowed
Overview
| 1. | Most objects swallowed will be eliminated naturally | |
| 2. | Sharp objects/objects like battery are dangerous | |
| 3. | Sharp objects should be removed | |
| 4. | Can happen to all ages | |
| 5. | Common in children of 1-3 years |
Causes
| 1. | Certain food like popcorn | |
| 2. | Coins | |
| 3. | Small toys | |
| 4. | Small objects like buttons, beads |
Symptoms
| 1. | Coughing | |
| 2. | Difficulty in breathing | |
| 3. | Wheezing |
Treatment
| 1. | If breathing is difficult, do Heimlich maneuver | |
| 2. | Seek medical help as quickly as possible | |
| 3. | On someone else Stand behind the person Stand behind the person Tilt the person a little forward Tilt the person a little forward Make a fist with one hand Make a fist with one hand Place it just above the navel Place it just above the navel Hold the fist with the other hand Hold the fist with the other hand Give a hard upward thrust into the abdomen Give a hard upward thrust into the abdomen Repeat if required Repeat if required |
|
| 4. | On Oneself Make fist with one hand Make fist with one hand Place fist above navel Place fist above navel Hold it with other hand Hold it with other hand Bend over a hard surface like a chair Bend over a hard surface like a chair Hold the fist with the other hand Hold the fist with the other hand Give hard upward thrust Give hard upward thrust Repeat if required Repeat if required |
Prevention
| 1. | Do not give potentially dangerous food to children | |
| 2. | Give small pieces of food to children | |
| 3. | Avoid laughing / talking when eating |
Fracture
What is fracture?
| 1. | A broken or cracked bone | |
| 2. | Occurs when pressure is applied to bone | |
| 3. | Occurs with / without displacement of bone fragments |

Types
| 1. | Open fracture: Skin breaks causing open wound | |
| 2. | Closed fracture: Skin not broken | |
| 3. | Complicated fractures: Damage of adjacent organs | |
| 4. | Stress fracture: Hairline crack due to repeated stress | |
| 5. | Greenstick fracture: In children's flexible bones |
Symptoms
| 1. | Severe pain | |
| 2. | Difficulty in movement | |
| 3. | Swelling/ bruising / bleeding | |
| 4. | Deformity / abnormal twist of limb | |
| 5. | Tenderness on applying pressure |
First-aid
| 1. | Depends on type & location of fracture | |
| 2. | For open fractures Control bleeding before treatment Control bleeding before treatment Rinse and dress the wound Rinse and dress the wound |
|
| 3. | For open / closed fractures Check the breathing Check the breathing  Calm the person Calm the person Examine for other injuries Examine for other injuries Immobilize the broken wound Immobilize the broken wound Apply ice to reduce pain / swelling Apply ice to reduce pain / swelling Consult a doctor Consult a doctor |
DO NOT
| 1. | Massage the affected area | |
| 2. | Straighten the broken bone | |
| 3. | Move without support to broken bone | |
| 4. | Move joints above / below the fracture | |
| 5. | Give oral liquids / food |
Prevention
| 1. | Wear protective pads / helmets when driving |
Teach children / practice, safe habits
Frost Bite
Overview
| 1. | Frostbite is damage caused by extreme cold to skin / tissues | |
| 2. | At -15C or below, blood vessels constrict to preserve body temperature | |
| 3. | When this state persists, tissue injury occurs | |
| 4. | Frost bite usually affects tissues which are distant from the heart | |
| 5. | It also occurs in tissues that are most exposed to cold | |
| 5. | The organs that are usually affected are - Nose Nose  Ears Ears Fingers Fingers Toes Toes |
|
| 6. | Care should be taken to prevent permanent tissue damage |
Risk Factors
| 1. | Diabetes | |
| 2. | Peripheral neuropathy | |
| 3. | Use of beta-blockers |
Symptoms
| 1. | Skin Discolorations | |
| 2. | Loose skin | |
| 3. | Tingling/burning sensation | |
| 4. | Partial/Complete numbness | |
| 5. | In severe cases, Dry gangrene followed by amputation Dry gangrene followed by amputation |
Treatment
| 1. | Get medical help as soon as possible. Meanwhile | |
| 2. | Wrap the affected area using clean cloth | |
| 3. | If no medical help is forthcoming - Move the victim to a warm place Move the victim to a warm place Treat hypothermia first. Cover the person well Treat hypothermia first. Cover the person well  Keep the frost-bitten site in warm but not in hot water Keep the frost-bitten site in warm but not in hot water This should be done till sensations returns This should be done till sensations returns |
Steps to Avoid
| 1. | Do not rub / massage the affected area | |
| 2. | Avoid treatment if a second round of cold exposure is anticipated | |
| 3. | Treatment followed by freezing causes extensive damage |
Prevention
| 1. | Avoid - Extreme cold Extreme cold Wet clothes Wet clothes  Chilly Wind Chilly Wind |
|
| 2. | During cold weather, wear several layers of clothing | |
| 3. | Wear accessories like- Mittens, not gloves Mittens, not gloves Two pairs of socks Two pairs of socks Hat / scarves to cover both ears well Hat / scarves to cover both ears well |
|
| 4. | Get enough food and rest | |
| 5. | Avoid alcohol immediately before exposure to cold | |
| 6. | Avoid cotton clothing |
Gastric Problems
What are Gastric Problems?
| 1. | Occurs in stomach / oesophagus | |
| 2. | Disturbance of gastric mucosa leads to acid secretion | |
| 3. | Acids contact stomach nerve endings | |
| 4. | Causes pain / discomfort |
Types
| 1. | May be acute / chronic | |
| 2. | Acute gastric problem reduces quickly | |
| 3. | Chronic gastric problems lead to ulcers |
Causes
| 1. | Physical and mental stress can also cause ulceration | |
| 2. | Causes of gastric mucosa inflammation: Acidic foods Acidic foods Alcohol Alcohol Smoking Smoking Stress Stress Drugs Drugs |
Drugs which causes gastric trouble
| 1. | Aspirin | |
| 2. | Nicotine | |
| 3. | Corticosteroids | |
| 4. | Erythromycin | |
| 5. | Beta- Blockers |
Symptoms
| 1. | Constant Pain | |
| 2. | Indigestion | |
| 3. | Nausea | |
| 4. | Vomiting | |
| 5. | Loss of appetite | |
| 6. | Diarrhea |
Avoid
| 1. | Hot Spicy foods | |
| 2. | Alcohol | |
| 3. | Smoking | |
| 4. | Excessive eating | |
| 5. | Large meals before bed | |
| 6. | Fatty food | |
| 7. | Pulse | |
| 8. | Late nights |
Treatment
| 1. | Acute problems resolve spontaneously | |
| 2. | Chronic problems should be treated | |
| 3. | Drugs for treatment include: Antacids Antacids H2 antagonists H2 antagonists Proton pump inhibitors Proton pump inhibitors |
|
| 4. | Timely meals releives pain due to ulcers | |
| 5. | Consult - Gastroenterologist. |
Gastroenteritis
Overview
| 1. | Gastroenteritis is inflammation of stomach and intestines | |
| 2. | Can affect- any one, any age, any time | |
| 3. | Symptoms prominent in children | |
| 4. | Depending on cause, it may last for a day or a week | |
| 5. | Use of drugs like aspirin can increase the risk |
Causes
| 1. | Bacteria contaminated food / water | |
| 2. | Viral infection | |
| 3. | Stress | |
| 4. | Irregular/ improper diet | |
| 5. | Tobacco or substance abuse | |
| 6. | Reaction to a new food | |
| 7. | Reaction to medication |
Symptoms
| 1. | Vomiting | |
| 2. | Nausea | |
| 3. | Diarrhea | |
| 4. | Cramps/Abdominal pain | |
| 5. | Dehydration | |
| 6. | Weakness | |
| 7. | Fever/Chills, occasionally |
Treatment
| 1. | Adequate rest is advised | |
| 2. | Drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration | |
| 3. | Gradually eat easy -to-digest food | |
| 4. | Avoid diary products | |
| 5. | Avoid eating if nauseated | |
| 6. | Do not give water to a child with gastroenteritis | |
| 7. | Give other prescribed rehydration liquids | |
| 8. | Or give a mixture of salt and glucose in water | |
| 9. | Consider nursing the baby | |
| 10. | Consider acetaminophen for relief | |
| 11. | Avoid acetaminophen in case of liver disease | |
| 12. | Avoid aspirin |
Consult a doctor
| 1. | Vomiting/Diarrhea persists | |
| 2. | Diarrhea is bloody | |
| 3. | Acute dehydration occurs | |
| 4. | Fever persists |
HEADACHE
Overview
| 1. | A condition where pain occurs in the head | |
| 2. | Most common of pain complaints | |
| 3. | Majority of headaches harmless, require no treatment | |
| 4. | Some are indications of an underlying disorder |
Causes
| 1. | Tension | |
| 2. | Stress | |
| 3. | Straining the eye | |
| 4. | Sinus infection | |
| 5. | Dehydration | |
| 6. | Ice cream | |
| 7. | Sex | |
| 8. | Thunder | |
| 9. | Withdrawal from caffeine/drugs | |
| 10. | Brain related  Aneurysms Aneurysms Tumours Tumours Meningitis Meningitis Encephalitis Encephalitis Head injury Head injury |

Types
| 1. | Vascular headache  e.g. - Migraine, fever headaches, high blood pressure e.g. - Migraine, fever headaches, high blood pressure Pain on one/both side of head Pain on one/both side of head Stomach upset Stomach upset Difficulty in seeing Difficulty in seeing Common in women Common in women |
|
| 2. | Muscular headache e.g. Tension headache e.g. Tension headache Tightening of facial/neck muscles Tightening of facial/neck muscles Radiate to forehead Radiate to forehead |
|
| 3. | Cervicogenic headache e.g Spondylitis e.g Spondylitis |
|
| 4. | Inflammatory headaches e.g Sinusitis e.g Sinusitis |
Treatment
| 1. | Most headaches treated with pain killer | |
| 2. | Common medications- actaminophen/parasitamol/aspirin | |
| 3. | Tension headache treated by lowering body temperature This is achieved by taking a cool shower This is achieved by taking a cool shower |
|
| 4. | If recurrent, keep a headache diary This helps to identify the cause This helps to identify the cause |
|
| 5. | Chronic use of painkillers causes 'rebound headaches' | |
| 6. | Complementary treatments like chiropractic care, effective |
Consult a doctor
| 1. | If - Headache is recurrent and persistent | |
| 2. | If - Headache occurs with Fever/convulsions Fever/convulsions Memory loss/confusion Memory loss/confusion Loss of consciousness Loss of consciousness Stiff Neck Stiff Neck |
Prevention
| 1. | Caffeine, a vasoconstrictor, is used to prevent severe migraine | |
| 2. | Supplements with magnesium, vit B12 and Q10 used for prevention |
Head Trauma
Overview
| 1. | Head trauma is an injury that affects the brain / skull | |
| 2. | Injuries range from minor to serious | |
| 3. | Head injury may be 'closed' or 'penetrating' | |
| 4. | 'Closed'-when head hits against a blunt object | |
| 5. | These injuries lead to concussion | |
| 6. | 'Penetrating' - an object penetrates skull and enters brain |
Causes
| 1. | Road traffic accidents | |
| 2. | Accidents at home / work | |
| 3. | Assault | |
| 4. | Fall | |
| 5. | Sports |
Symptoms
| 1. | Loss of consciousness - for short or long duration | |
| 2. | Bleeding | |
| 3. | Vomiting | |
| 4. | Fluid discharge from nose | |
| 5. | Loss of hearing, vision, taste, smell | |
| 6. | Speech-related problems | |
| 7. | Irregular heart beat | |
| 8. | Seizures | |
| 9. | Paralysis | |
| 10. | Coma | |
| 11. | Change in personality | |
| 12. | Mental health-related problems |
Treatment
| 1. | For mild injury- Apply ice to injured area to minimize swelling Apply ice to injured area to minimize swelling The size of the bump is not related to the severity of injury The size of the bump is not related to the severity of injury Observe the patient carefully for signs of bleeding Observe the patient carefully for signs of bleeding |
|
| 2. | For moderate to severe injury- Check the patient's breathing pattern Check the patient's breathing pattern If necessary do Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) If necessary do Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) In case of bleeding, press area with a clean cloth In case of bleeding, press area with a clean cloth If the cloth soaks, place a fresh cloth over the first one If the cloth soaks, place a fresh cloth over the first one Do not remove debris from the wound Do not remove debris from the wound If person is vomiting turn on the side and lower the head If person is vomiting turn on the side and lower the head To minimize spine injury - hold head, neck and body in one line To minimize spine injury - hold head, neck and body in one line Immobilize the patient Immobilize the patient If unconscious, treat it like a spinal injury If unconscious, treat it like a spinal injury Keep the head in alignment with spine Keep the head in alignment with spine Get immediate medical help Get immediate medical help |
Consult a Doctor
| 1. | When the following occur seek medical help | |
| 2. | Bleeding | |
| 3. | Fluid discharge from nose, mouth, ears | |
| 4. | Vomiting | |
| 5. | Loss of consciousness | |
| 6. | Confusion / Restlessness / Irritability | |
| 7. | Slurred speech / Convulsion | |
| 8. | Blurred Vision | |
| 9. | Low breathing | |
| 10. | Low blood pressure / Severe headache | |
| 11. | Fracture / Stiff neck | |
| 12. | Loss of sensory abilities | |
| 13. | Inability to move one or more limbs |
Steps to Avoid
| 1. | Avoid shaking or moving a person who has head injuries | |
| 2. | Avoid washing the wound or removing debris | |
| 3. | Do not remove helmet in case of head injury | |
| 4. | Do not consume alcohol immediately after a head injury | |
| 5. | Do not pick up a fallen child with head injury |
Prevention
| 1. | Do not indulge in drunken driving | |
| 2. | Practice safe methods while driving / sporting / other activities | |
| 3. | Always follow safety rules | |
| 4. | Supervise the activities of children |
Heart Attack
What is heart attack?
| 1. | Occurs when blood supply to vital organs gets blocked | |
| 2. | >50years / menopausal women at greater risk | |
| 3. | Occurs with / without chest pain | |
| 4. | Sudden arrest of breathing / heart function | |
| 1. | May result in cardiopulmonary arrest | |
| 2. | Clot in the arteries blocks blood supply | |
| 3. | Occurs due to: Deposits of calcium / cholesterol Deposits of calcium / cholesterol Hereditary factors Hereditary factors Tobacco Tobacco Obesity Obesity High blood pressure High blood pressure Emotional stress Emotional stress Inflammatory disease of arteries Inflammatory disease of arteries Trauma / disease of heart Trauma / disease of heart |

Symptoms
| 1. | Chest pain | |
| 2. | Shoulder/arm pain | |
| 3. | Shortness of breath | |
| 4. | Sweating | |
| 5. | Heartburn | |
| 6. | Nausea | |
| 7. | Abdominal pain |
First aid
| 1. | Try to relax | |
| 2. | Loosen tight clothes | |
| 3. | Take medicines if any | |
| 4. | Pain subsides within 3 min of medicine intake | |
| 5. | If not, see a doctor. | |
| 6. | Give artifical respiration if required | |
| 7. | Give Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR): If no pulse is detected If no pulse is detected By placing palm on chest to pump By placing palm on chest to pump |
|
| 6. | 15 pumps are followed by 2 artificial respiration | |
| 7. | Continue till ambulance / doctor arrives |
Prevention
| 1. | Routine health check-up | |
| 2. | Avoid stress | |
| 3. | Quit smoking / alcohol | |
| 4. | Eat sensibly | |
| 5. | Control blood pressure / diabetes | |
| 6. | Control weight |
Heat Cramps
Overview
| 1. | Heat exhaustion is a heat - related disorder | |
| 2. | Here, loss of fluids takes place | |
| 3. | This decreases blood flow to vital organs, leading to shock |
Causes
| 1. | Heat exhaustion caused by excessive heat | |
| 2. | Increased by overexertion / sweating / hot, humid climate |
Risk Factors
| 1. | Poor circulation | |
| 2. | Recurrent Illness | |
| 3. | Medications like diuretics / laxatives / anti histamines / anti depressants | |
| 4. | Young children and older people at risk, even when inactive |
Symptoms
| 1. | Weakness / dizziness | |
| 2. | Headache / nausea | |
| 3. | Cold / moist skin | |
| 4. | Paleness | |
| 5. | Dry tongue / thirst | |
| 6. | Vomiting | |
| 7. | Loss of appetite | |
| 8. | Excessive sweating | |
| 9. | Rapid / weak heart beat | |
| 10. | Fast / shallow breathing | |
| 11. | Muscle fatigue | |
| 12. | Cramps |
Treatment
| A. | Cooling the body
|
|||||||||||||
| B. | Hydrating
|
Consult A Doctor
| 1. | If the symptoms don't clear up in 30 minutes | |
| 2. | Seek emergency help in case of  Physical collapse Physical collapse Loss of consciousness Loss of consciousness |
Prevention
| 1. | Do not indulge in drunken driving | |
| 2. | Practice safe methods while driving / sporting / other activities | |
| 3. | Always follow safety rules | |
| 4. | Supervise the activities of children |
Heat Exhaustion
Overview
| 1. | Heat exhaustion is a heat - related disorder | |
| 2. | Here, loss of fluids takes place | |
| 3. | This decreases blood flow to vital organs, leading to shock |
Causes
| 1. | Heat exhaustion caused by excessive heat | |
| 2. | Increased by overexertion / sweating / hot, humid climate |
Risk Factors
| 1. | Poor circulation | |
| 2. | Recurrent Illness | |
| 3. | Medications like diuretics / laxatives / anti histamines / anti depressants | |
| 4. | Young children and older people at risk, even when inactive |
Symptoms
| 1. | Weakness / dizziness | |
| 2. | Headache / nausea | |
| 3. | Cold / moist skin | |
| 4. | Paleness | |
| 5. | Dry tongue / thirst | |
| 6. | Vomiting | |
| 7. | Loss of appetite | |
| 8. | Excessive sweating | |
| 9. | Rapid / weak heart beat | |
| 10. | Fast / shallow breathing | |
| 11. | Muscle fatigue | |
| 12. | Cramps |
Treatment
| A. | Cooling the body
|
|||||||||||||
| B. | Hydrating
|
Consult A Doctor
| 1. | If the symptoms don't clear up in 30 minutes | |
| 2. | Seek emergency help in case of  Physical collapse Physical collapse Loss of consciousness Loss of consciousness |
Prevention
| 1. | Do not indulge in drunken driving | |
| 2. | Practice safe methods while driving / sporting / other activities | |
| 3. | Always follow safety rules | |
| 4. | Supervise the activities of children |
Heat Stroke
Overview
| 1. | Heat stroke is the most severe of all heat-related illness | |
| 2. | Heat stroke could be life - threatening |
Causes
| 1. | Cooling mechanism of the body fails due to  Excessive humidity Excessive humidity Extreme heat Extreme heat Activity in the hot sun Activity in the hot sun |
|
| 2. | Internal body temperature rises, leading to stroke |
Risk Factors
| 1. | Dehydration | |
| 2. | Infants & older people | |
| 3. | People who work long hours, outdoor | |
| 4. | Obesity | |
| 5. | Impairment in sweat gland function | |
| 6. | Cardiovascular disorder | |
| 7. | Medications |
Symptoms
| 1. | Body temperature, greater than 1040F | |
| 2. | Head ache | |
| 3. | Dizziness | |
| 4. | Confusion | |
| 5. | Disorientation | |
| 6. | Fatigue | |
| 7. | Hot dry skin | |
| 8. | Skin is moist, if stroke is due to exertion | |
| 9. | Rapid / shallow breathing | |
| 10. | Absence of sweating | |
| 11. | Fluctuating blood pressure | |
| 12. | Irritability | |
| 13. | Confusion | |
| 14. | Lack of consciousness / coma |
Treatment
| 1. | Remove the person to a shady place | |
| 2. | Cool the person by sponging with wet towel | |
| 3. | Apply ice packs in armpits and groin | |
| 4. | Water with electrolyte, fruit / vegetable juice should be given | |
| 5. | Victim must be rested |
Prevention
| 1. | Avoid outdoor activity during excessive heat | |
| 2. | Drink plenty of fluids when working outdoors | |
| 3. | During outdoor activity, splash your body frequently with water | |
| 4. | Avoid alcohol / coffee / soda / alcohol | |
| 5. | Wear light weight, light- colored, loose-fitting clothes | |
| 6. | Protect yourself from the sun by wearing sun glasses and hat |
Human Bites
Overview
| 1. | Usually occurs when one person bites another | |
| 2. | Comes in contact with another person's teeth | |
| 3. | Can be more dangerous than animal bite | |
| 4. | Human bites has increased risk of infection | |
| 5. | This is due to microbes present in the mouth | |
| 6. | Risk of injury to tendons and joints also present | |
| 7. | Very common among children |
Symptoms
| 1. | Puncture wounds on skin | |
| 2. | Skin Breaks | |
| 3. | Cuts | |
| 4. | Bleeding |
Treatment
| 1. | Calm the victim | |
| 2. | If bleeding is not severe, wash the wound | |
| 3. | Use a mild soap | |
| 4. | Clean the wound in running water for 3-5 min | |
| 5. | Apply an antibiotic cream | |
| 6. | Dress the wound using sterile gauze | |
| 7. | If the bleeding is severe, apply pressure to stop bleeding | |
| 8. | Keep the wounded part in a slightly raised position | |
| 9. | Get medical attention immediately | |
| 10. | If not covered for tetanus - an injection is recommended |
Consult a Doctor
| 1. | All human bites must be evaluated by the doctor especially in case of-  Broken skin Broken skin Redness Redness Swelling Swelling Pain Pain Pus formation Pus formation If wound occurs near eye, on the face If wound occurs near eye, on the face If victim has weak immune system (as in AIDS, Cancer) If victim has weak immune system (as in AIDS, Cancer) |
Steps to Avoid
| 1. | Do not ignore human bites | |
| 2. | Avoid placing the wound in the mouth |
Prevention
| 1. | Avoid placing hand near the mouth of a seizure-affected person | |
| 2. | Take caution to prevent your child from developing biting habit |
Insect Bites and Stings
Overview
 |
Insect bites are, mostly, not severe | |
 |
Sometimes they cause a severe allergic reaction, anaphylaxis | |
 |
Anaphylaxis is life-threatening if not treated on time | |
 |
Sting of bees, wasps, hornets / bite of fire ants, painful | |
 |
Bites of insects, like mosquitoes, cause itching | |
 |
The bite of a black widow spider can be fatal, if left untreated |
Causes
Examples of biting insects
 |
Mosquitoes | |
 |
Fleas | |
 |
Mites | |
 |
Spiders |
Examples of stinging insect
 |
Bees | |
 |
Wasps | |
 |
Hornets |
Symptoms
 |
Localized Pain | |
 |
Swelling | |
 |
Redness | |
 |
Itching | |
 |
Numbness | |
 |
Burning | |
 |
Tingling sensation | |
 |
Breathlessness | |
 |
Weakness |
Treatment
 |
Remove the stinger using a straight- edged object | |
 |
Wash the area thoroughly with soap and water | |
 |
Place ice wrapped in a cloth on the affected area | |
 |
Repeat after every 10 minutes | |
 |
Apply a gentle cream to prevent itching | |
 |
Take anti histamines if necessary | |
 |
Observe for signs of infection like pain, redness or swelling |
In case of emergency-
 |
Try to keep the person calm | |
 |
Check the person's breathing | |
 |
Remove constricting items, like rings, from finger/nose/ears | |
 |
Do Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR), if necessary | |
 |
If the person is carrying an emergency kit, use it | |
 |
If required, treat the person for signs of shock | |
 |
Seek medical help as soon as possible |
Consult a Doctor in case of the following, seek medical help
 |
Wheezing | |
 |
Swelling on the face | |
 |
Difficulty in breathing | |
 |
Tight feeling in the throat | |
 |
Body turning blue |
Steps to Avoid
 |
Do not remove the stinger using a tweezer | |
 |
Do not apply a tourniquet | |
 |
Aspirin, pain medications, should not be given unless advised by a doctor |
Prevention
 |
Avoid placing hand near the mouth of a seizure-affected person | |
 |
Take caution to prevent your child from developing biting habit |
Fainting
About Fainting
 |
Fainting occurs due to decreased blood supply to brain | |
 |
A fainting spell is usually very brief | |
 |
It may or may not have medical significance |
Common Causes
 |
Anxiety | |
 |
Emotional upset | |
 |
Stress | |
 |
Severe pain | |
 |
Skipping meals | |
 |
Standing up too fast | |
 |
Standing for a long time in a crowd | |
 |
Some medications | |
 |
Diabetes | |
 |
Blood Pressure |
Symptoms
Before fainting, a person may experience the following:
 |
Nausea | |
 |
Giddiness | |
 |
Excessive sweating | |
 |
Dim vision | |
 |
Rapid heart beat or palpitations |
Treatment
 |
Fainting is a medical emergency, till proven otherwise | |
 |
When a person feels faint- Make them sit down or lie down | |
 |
If sitting, position head between knees | |
 |
When a person faints, position him on his back | |
 |
Check to see if airways are clear | |
 |
Restore blood flow by -Loosening clothing/belts/collars | |
 |
Elevate feet above head level | |
 |
Patient should become normal within a minute | |
 |
If not, seek medical help | |
 |
Check if breathing/pulse is normal | |
 |
If not, do Cardio-pulmonary resuscitation (CPR) Prevention | |
 |
When symptoms appear, lie down | |
 |
Try do avoid stress and anxiety | |
 |
Carefully evaluate your medications | |
 |
Take care of underlying medical conditions |
Nose Bleed
Overview
 |
A nose bleed occurs when a small vein, along the lining of nose, bursts | |
 |
Most nosebleeds look scary, but are harmless | |
 |
Can be treated at home | |
 |
Common in children/elderly |

Causes
 |
Dryness | |
 |
Nose picking | |
 |
Blowing nose with force | |
 |
Use of medications, like aspirin | |
 |
Introducing objects into nose (mostly children) | |
 |
Injuries | |
 |
Allergies | |
 |
Infections | |
 |
High BP | |
 |
Atherosclerosis | |
 |
Blood-clotting disorders | |
 |
Use of cocaine |
Symptoms
 |
Bleeding from nose | |
 |
Sometimes bleeding from ears/mouth too |
Types
| 1. | Anterior Nosebleed
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2. | Posterior Nosebleed
|
Treatment
 |
If your nose bleeds, | |
 |
Sit down and lean forward | |
 |
Using your thumb & index finger, squeeze soft part of nose | |
 |
This part is between end of nose and the bridge of nose | |
 |
Continue holding till bleeding stops- | |
 |
Do not stop in-between | |
 |
If bleeding continues, hold for another 10 minutes | |
 |
If the patient is a child, divert attention by TV/Stories | |
 |
Avoid picking, blowing or rubbing nose for 2 days | |
 |
Place an ice pack on the bridge of nose |
Consult a Doctor
 |
The bleeding continues for more than 15 minutes | |
 |
The bleeding is caused by an injury | |
 |
You get nosebleeds often |
Prevention
 |
Keep fingernails short | |
 |
Quit smoking | |
 |
Open your mouth while sneezing | |
 |
Use a humidifier at night in case of dry weather |
Poisoning
Overview
 |
Poisons are substances that cause injury, illness or death | |
 |
These events are caused by a chemical activity in the cells | |
 |
Poisons can be injected, inhaled or swallowed | |
 |
Poisoning should be suspected if a person is sick for unknown reason | |
 |
Poor ventilation can aggravate Inhalation poisoning | |
 |
First aid is critical in saving the life of victims |

Causes
 |
Medications | |
 |
Drug overdose | |
 |
Occupational exposure | |
 |
Cleaning detergents/paints | |
 |
Carbon mono oxide gas from furnace, heaters | |
 |
Insecticides | |
 |
Certain cosmetics | |
 |
Certain household plants, animals | |
 |
Food poisoning (Botulism) |
Symptoms
 |
Blue lips | |
 |
Skin Rashes | |
 |
Difficulty in breathing | |
 |
Diarrhea | |
 |
Vomiting/Nausea | |
 |
Fever | |
 |
Head ache | |
 |
Giddiness/drowsiness | |
 |
Double vision | |
 |
Abdominal/chest pain | |
 |
Palpitations/Irritability | |
 |
Loss of appetite/bladder control | |
 |
Numbness | |
 |
Muscle twitching | |
 |
Seizures | |
 |
Weakness | |
 |
Loss of consciousness |
Treatment
 |
Seek immediate medical help | |
 |
Try and identify the poison if possible | |
 |
Check for signs like burns around mouth, breathing difficulty or vomiting | |
 |
Induce vomiting if poison swallowed | |
 |
In case of convulsions, protect the person from self injury | |
 |
If the vomit falls on the skin, wash it thoroughly | |
 |
Position the victim on the left till medical help arrives | |
 |
Seek immediate emergency help | |
 |
Get help before you attempt to rescue others | |
 |
Hold a wet cloth to cover your nose and mouth | |
 |
Open all the doors and windows | |
 |
Take deep breaths before you begin the rescue | |
 |
Avoid lighting a match | |
 |
Check the patient's breathing | |
 |
Do a CPR, if necessary | |
 |
If the patient vomits, take steps to prevent choking |
Steps to Avoid
 |
Avoid giving an unconscious victim anything orally | |
 |
Do not induce vomiting unless told by a medical personnel | |
 |
Do not give any medication to the victim unless directed by a doctor | |
 |
Do not neutralize the poison with limejuice/honey |
Prevention
 |
Store medicines, cleaning detergents, mosquito repellants and paints carefully | |
 |
Keep all potentially poisonous substances out of children's reach | |
 |
Label the poisons in your house | |
 |
Avoid keeping poisonous plants in or around house | |
 |
Take care while eating products such as berries, roots or mushrooms | |
 |
Teach children the need to exercise caution |
Puncture Wounds
Overview
 |
Puncture wounds are injuries caused by sharp objects | |
 |
These wounds carry dirt and germs deep into the tissues | |
 |
Increases the risk of infection | |
 |
Most wounds are minor and may be treated at home | |
 |
Some punctures are made by a health professional for disease treatment | |
 |
Even if the wound is closed, puncture wounds require treatment |
Risk Factors
 |
Health professionals | |
 |
Drug Abusers |
Causes
 |
Nails | |
 |
Needles | |
 |
Teeth | |
 |
Objects like ice picks, bullets | |
 |
Animals, especially pets |
Symptoms
 |
Pain | |
 |
Bleeding | |
 |
Bruising | |
 |
Swelling |
Treatment
 |
Stop the bleeding applying gentle pressure | |
 |
Clean the wound | |
 |
Try to remove embedded debris carefully | |
 |
Soak wound in warm water for 20 minutes | |
 |
This should be done 2-3 times a day | |
 |
Pat the area dry | |
 |
Apply an antibiotic cream | |
 |
Apply a bandage | |
 |
If the bandage needs to be changed, unwrap carefully | |
 |
If the bandage sticks to the body, use warm water to loosen itching | |
 |
Pat dry and apply fresh bandage | |
 |
Change the dressing regularly | |
 |
Try to keep the wound above the level of your heart, for 24 hrs | |
 |
This quickens healing | |
 |
Rest for 3-5 days | |
 |
Look out for infection | |
 |
Take a Tetanus Toxoid injection, if you have not taken it in 5 years |
Consult a Doctor
 |
Human/animal bite | |
 |
High temperature | |
 |
Bleeding | |
 |
Worsening Pain | |
 |
Numbness | |
 |
Swelling | |
 |
Redness | |
 |
Pus | |
 |
Bad odor |
Prevention
 |
Health professionals should wear gloves whenever required | |
 |
Be careful while handling needles/other sharp objects | |
 |
Exercise caution while handling pets |
Severe Bleeding
Overview
 |
Severe bleeding involves loss of large amount of blood | |
 |
This may occur externally through natural openings, like mouth | |
 |
A cut on the skin too can lead to bleeding | |
 |
Internal bleeding occurs due to an injury to blood vessel |
Causes
| 1. | Accidents/Falls | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. | Blow to the head | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3. | Injuries, like scalp wounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4. | Tooth Extraction | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5. | Certain medications | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6. | Illnesses like
|
Symptoms
 |
Discharge of blood from a wound | |
 |
Bruising | |
 |
Blood in stool/urine | |
 |
Blood coming from other areas, like mouth/ear |
Treatment
 |
Wash hands well before administering to patient | |
 |
Wear synthetic gloves | |
 |
Make the victim lie down | |
 |
Slightly elevate the legs | |
 |
If possible keep the affected area elevated | |
 |
Remove any obvious debris/particle | |
 |
Apply direct pressure using clean cloth/bandage | |
 |
Use hand if cloth is not available | |
 |
Apply pressure continuously for at least 20 minutes | |
 |
Do not remove the cloth to check the bleeding | |
 |
Hold the bandage in place using an adhesive tape | |
 |
If bleeding seeps through bandage, do not remove it | |
 |
Add extra bandage on top of the first one | |
 |
Apply direct pressure on the artery if necessary | |
 |
The pressure points for arm--below arm- pit/above elbow | |
 |
For leg--behind knee/near groin | |
 |
Squeeze the artery keeping finger flat | |
 |
Continue applying pressure on the wound | |
 |
Once bleeding stops immobilize the affected part | |
 |
See a doctor |
Consult a doctor
 |
If bleeding does not stop | |
 |
If bleeding occurs through nose, ears etc | |
 |
Coughing up blood | |
 |
Vomiting | |
 |
Bruising/deep wounds | |
 |
Abdominal tenderness | |
 |
Fracture | |
 |
Shock |
Steps To Avoid
 |
Do not try to replace a displaced organ | |
 |
Just cover the wound with a clean cloth | |
 |
Do not try to remove an embedded object |
Shock
Overview
 |
Shock is a life-threatening condition | |
 |
When vital organs fail to get enough blood, shock results |
Causes
 |
Severe infections | |
 |
Allergic reactions | |
 |
Heat Stroke | |
 |
Trauma | |
 |
Poisoning | |
 |
Injury |
Symptoms
 |
Cool, clammy skin | |
 |
Lackluster eyes | |
 |
Dilated pupils | |
 |
Vomiting/nausea | |
 |
Feeling weak | |
 |
Confusion | |
 |
Excitement | |
 |
Anxiety | |
 |
Shallow/ slow breathing or rapid/ deep breathing | |
 |
Weak and rapid pulse |
Treatment
Get emergency medical help. Meanwhile-
 |
Make the person lie down on the back | |
 |
Raise the legs above head level | |
 |
If raising the legs is painful, keep the person still | |
 |
Check for breathing | |
 |
If not breathing, do Cardio pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) | |
 |
Make the person comfortable by loosening tight clothes | |
 |
Cover the person with a blanket | |
 |
If vomiting or bleeding from mouth -turn the patient on the side | |
 |
Do not feed the person orally |
Prevention
 |
Learn ways of preventing shock | |
 |
If you have a known allergy, carry emergency kits | |
 |
Teach family and friends how to use the kit |
Snake Bites
Overview
 |
Thousands suffer from snake bites, globally, every year | |
 |
People who live near wilderness/trekkers - more prone | |
 |
Even bite from a harmless snake can cause allergic reaction |
Causes
Some common venomous snakes include -
 |
Viper | |
 |
Cobra | |
 |
Rattle snake | |
 |
Water moccasin | |
 |
Coral snake | |
 |
Copper head |
Symptoms
 |
Fang marks | |
 |
Swelling/severe pain at the site | |
 |
Bloody discharge from wound | |
 |
Burning | |
 |
Diarrhea | |
 |
Excessive sweating | |
 |
Blurred vision | |
 |
Numbness/tingling sensation | |
 |
Increased thirst | |
 |
Vomiting | |
 |
Fever | |
 |
Loss of muscle co-ordinations | |
 |
Convulsions | |
 |
Rapid pulse | |
 |
Weakness/Dizziness/Fainting |
Treatment
| A. | Seek Medical help as soon as possible. Meanwhile -
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| B. | Monitor for pulse, respiration and blood pressure |
Prevention
 |
Do not attempt to kill a snake. | |
 |
If you spot a snake, leave it alone | |
 |
While hiking or in the woods, stay out of tall grass | |
 |
Do not put your hand into pits/crevices during treks | |
 |
Exercise caution while climbing rocks |
Spinal Cord Injury
Overview
 |
Spinal cord injury is otherwise called 'myelopathy' | |
 |
It results in an injury to the nerve fibers in the cord | |
 |
Can cause loss of physical sensation and mobility | |
 |
Spinal cord remains intact in most of the injuries | |
 |
Complete injury causes no movement/sensation below injury | |
 |
Incomplete injury-retains some movement/sensation below injury | |
 |
Physical therapy, ventilators, wheel chairs often required |
Causes
| 1. | Automobile accidents | |||||||||||||
| 2. | Diving accidents | |||||||||||||
| 3. | Falls | |||||||||||||
| 4. | Shot by a gun | |||||||||||||
| 5. | Conditions like
|
Symptoms
 |
Loss of sensation | |
 |
Loss of motor functions | |
 |
Loss of bowel/bladder functions | |
 |
Sexual function can get affected | |
 |
Loss of involuntary functions, like breathing | |
 |
Inability to control rate of heart beat | |
 |
Inability to sweat | |
 |
Chronic pain |
Treatment
Seek medical help or call for an ambulance as soon as possible. Meanwhile-
 |
Move the person, if surrounding is not safe | |
 |
Immobilize the head, neck and body on both sides | |
 |
Movements may dislocate vertebra and cause further injury | |
 |
If there is no sign of breathing, perform CPR | |
 |
Do not tilt head backward during CPR |
Prevention
 |
Always wear a seat belt while driving | |
 |
Use special seat belts for children and babies | |
 |
Do not drink and drive | |
 |
Do not dive into a shallow pool area |
Sprain
Overview
 |
Sprain is the stretch/tear of ligament connecting bones | |
 |
Occurs in both the upper & lower part of the body | |
 |
Most common sites - ankle/wrists/knee |
Causes
 |
Trauma/accidents | |
 |
Lifting heavy objects | |
 |
Sporting injuries |
Symptoms
 |
Pain | |
 |
Swelling | |
 |
Lumps other than swelling | |
 |
Bruising/redness at site of injury | |
 |
Numbness | |
 |
Inability to move the joint |
Treatment
 |
Apply a cold compress to injured area for 20 min | |
 |
This may be done 4-8 times a day | |
 |
Use a plastic bag with crushed ice, wrapped in a towel | |
 |
Use compression bandages to reduce swelling | |
 |
Keep the injured leg elevated on a pillow | |
 |
Take anti inflammatory pills if necessary | |
 |
Take rest for the recommended period | |
 |
When pain/swelling is diminished, do recommended exercises |
Consult a doctor
If the following occurs-
 |
Severe pain/numbness | |
 |
Inability to move the joint | |
 |
Inability to assess the severity of injury |
Steps To Avoid
If the following occurs-
 |
Do not return to normal activities if not completely cured | |
 |
This could lead to the problem turning chronic |
Prevention
 |
Avoid exercising/sporting when tired | |
 |
Eat a well balanced meal-for healthy muscles | |
 |
Avoid unhealthy weight gain | |
 |
Exercise daily-particularly stretching exercises | |
 |
Do warm-up before exercising | |
 |
Practice safety measures, like avoiding clutter | |
 |
Run on even surface | |
 |
Do not wear ill-fitting shoes |
Stroke
Overview
 |
Stroke is also called 'Cerebrovascular Accident' | |
 |
It is an acute neurological injury | |
 |
It may be due to blood clot (ischemic) or bleeding (hemorrhagic) | |
 |
Leads to stoppage of blood supply to a part of brain | |
 |
Oxygen supply is decreased | |
 |
This initiates 'ischemic cascade'-causes brain cell death/damage | |
 |
This results in a cerebral stroke |
Causes/Risks
 |
High Blood Pressure | |
 |
Diabetes | |
 |
Cigarette smoking | |
 |
Heart Disease |
Symptoms
 |
Numbness/weakness of an arm/leg/face/one side of body | |
 |
Sudden confusion in speaking/understanding speech | |
 |
Impaired vision in one or both eyes | |
 |
Sudden headache | |
 |
Loss of balance/co-ordination | |
 |
Dizziness |
Treatment
 |
If you suspect stroke, call emergency medical help | |
 |
Reassure the patient | |
 |
Lay the patient down with head and shoulders slightly elevated | |
 |
If patient is not breathing well do a CPR | |
 |
Place the patient on the left side if breathing/not responsive | |
 |
Keep the chin slightly extended |
Steps To Avoid
 |
Never give a suspected stroke victim anything to eat/drink | |
 |
Do not permit the victim to move/td> |
Prevention
 |
Do regular checkups for BP | |
 |
Eat food with less salt | |
 |
Exercise regularly | |
 |
Eat a balanced, healthy diet | |
 |
Take the BP pills regularly |
Sun Burn
Overview
 |
Sunburn is a burn of the skin | |
 |
Results from overexposure to the sun | |
 |
Normal exposure results in the production of Vitamin D | |
 |
Most of us become sun burnt at some time in life | |
 |
Sunburn causes a lot of discomfort | |
 |
It can cause premature ageing/cancer | |
 |
Common in children/young adults |
Causes
 |
Sun's ultraviolet rays during outdoor activities | |
 |
Tanning beds |
Risk factors
 |
Light-skinned or fair-haired people | |
 |
Recent exposure to sun | |
 |
Prior skin injury | |
 |
Infections like Herpes, Porphyria | |
 |
Certain Medications like antibiotics, anti-psoriatic drugs |
Symptoms
The skin injury begins within 30 minutes of exposure to the sun
 |
Redness of the skin | |
 |
Irritation | |
 |
Blisters | |
 |
Pain | |
 |
Skin burning | |
 |
Skin loss | |
 |
Dehydration | |
 |
Flu-like symptoms | |
 |
Infection | |
 |
Fever | |
 |
If very severe, shock leading to death may occur |
Treatment
Self-Help
| 1. | Get out of the sun | ||||||||||||||||
| 2. | Cover the exposed area | ||||||||||||||||
| 3. | Take a cool bath | ||||||||||||||||
| 4. | Use a cool compress available commercially like, Burow solution
|
||||||||||||||||
| 5. | Apply aloe-based solution | ||||||||||||||||
| 6. | Avoid using oils, bath salts, perfumed lotions etc | ||||||||||||||||
| 7. | Avoid scrubbing/shaving | ||||||||||||||||
| 8. | Use a gentle towel | ||||||||||||||||
| 9. | Stay out of the sun while sun burnt |
Consult a Doctor
In case of-
 |
Pain | |
 |
Headache/confusion | |
 |
Blisters | |
 |
Nausea/vomiting | |
 |
Loss of consciousness | |
 |
Sunburn being present along with other medical condition |
Prevention
 |
Wear hats, long-sleeved dress, long pants while out in the sun | |
 |
Try to avoid exposure to sun | |
 |
Use sun-block creams during exposure to sun | |
 |
Select a suitable SPF number for the sun block cream | |
 |
Sun Blocks should be reapplied every 2-3 hours | |
 |
Avoid tanning beds |
Tick Bite
Overview
 |
Ticks are small, insect-like creatures | |
 |
They may be small or as large as the size of an eraser | |
 |
They are usually found in the fields and woods | |
 |
They attach themselves to humans/ pets /other animals | |
 |
Once on the body, they move to other warm, moist areas | |
 |
Favorite haunts include hair, armpit and groin | |
 |
Once firmly attached to the body, they begin to suck blood | |
 |
They can cause harmless or harmful conditions |
Symptoms
 |
Rashes, redness, itching | |
 |
Swelling at the site | |
 |
Muscle/joint pain | |
 |
Inflammation of the joints | |
 |
Swollen lymph node | |
 |
Flu-like symptoms | |
 |
Fever |
Symptoms that need emergency treatment--
 |
Severe headache | |
 |
Chest pain | |
 |
Palpitations | |
 |
Difficulty in breathing | |
 |
Paralysis |
Treatment
 |
Remove the tick carefully by holding head, using a tweezer | |
 |
Remove the whole tick | |
 |
Do not crush the tick | |
 |
Put the tick into a bottle and seal | |
 |
This is to provide your doctor with information | |
 |
Use soap and water to wash the affected area | |
 |
Wash your hands thoroughly | |
 |
Seek medical help if you are unable to remove the tick |
Prevention
 |
When walking in woods or tall grass wear clothes and shoes that cover you fully | |
 |
Keep the shirt tucked into pants | |
 |
Pull socks over the pants to cover feet well | |
 |
Wear light-colored clothes to spot ticks easily | |
 |
Spray insect repellents on your clothes | |
 |
While outside, check your clothes frequently for ticks | |
 |
On your return home, inspect yourself thoroughly for ticks |
Tooth Ache
Overview/Causes
 |
Tooth ache is primarily caused by tooth decay | |
 |
Bacteria flourishes on sugar/starch in food particles inside mouth | |
 |
A sticky plaque is then formed on teeth surface | |
 |
The bacteria in the plaque produces acid | |
 |
This acid erodes the enamel or hard covering of the teeth | |
 |
This creates a cavity | |
 |
The first sign of tooth decay is tooth ache | |
 |
This occurs on eating something very cold/very hot/sweet | |
 |
Tooth ache can also be caused by injury/trauma | |
 |
Tooth ache can occur in children and adults |

Symptoms
Pain in the tooth radiates to jaw, cheek, ear
 |
Pain while chewing | |
 |
Increased sensitivity to hot/cold things | |
 |
Swelling in the jaw | |
 |
Discharge/Bleeding from tooth or gums |
Treatment
 |
Use a floss to remove any particle lodged between teeth | |
 |
Learn flossing from a dentist | |
 |
Take a pain relieving tablet | |
 |
Apply benzocaine containing antiseptic | |
 |
Applying clove oil also might help | |
 |
Do not place aspirin directly against the gums | |
 |
This might lead to burning of gum tissue |
Consult a Doctor
 |
Tooth ache persists | |
 |
Fever occurs with the ache | |
 |
Difficulty in breathing occurs | |
 |
Difficulty in swallowing occurs |
Prevention
 |
Brush teeth after every meal | |
 |
Floss regularly | |
 |
Visit your dentist twice a year | |
 |
Wear a mouth gear while playing | |
 |
Avoid smoking as it worsens dental conditions | |
 |
Eat a balanced meal with reduced starch/sugar content |
Tooth Loss
Overview
 |
Tooth loss can happen due to various factors | |
 |
Occurs both in adults and children | |
 |
In some cases it can be prevented |
Causes
 |
Injuries, | |
 |
Trauma |
Predisposing conditions:
 |
Thumb sucking, | |
 |
Mouth breathing | |
 |
Pacifier usage | |
 |
Poor oral hygiene/Tooth decay | |
 |
Mismatched jaw/teeth | |
 |
Genetic factors |
Symptoms
 |
Pain | |
 |
Blood loss/discharge | |
 |
Feeling of weakness |
Treatment
Seek a dentist's help on an emergency basis. To replace the fallen tooth, follow these steps-
 |
Gently hold the fallen tooth by the top | |
 |
Do not touch the roots | |
 |
Rinse the tooth gently | |
 |
Avoid running water | |
 |
Try to replace tooth in socket | |
 |
If you cannot replace, place it in whole milk or your saliva | |
 |
You may also place it in mild salt solution-1/4 tsp salt in 1 quart water |
Prevention
 |
While sporting, wear a mouth guard | |
 |
Treat gum disease at the earliest | |
 |
Take care of teeth by brushing/flossing regularly | |
 |
Use an antiseptic mouth wash regularly |
Electric shock
Overview
 |
Injuries caused when electric current passes through body | |
 |
Source may be natural or man-made |
What happens during electric shock?
 |
Makes you fall down | |
 |
Muscle contraction | |
 |
Seizures | |
 |
Dehydration | |
 |
Burns | |
 |
Fractures | |
 |
Clotting of blood | |
 |
Tissue death (narcosis) | |
 |
Respiratory/Heart/Kidney failure |
Steps to follow
 |
Do not attempt to move the victim from current source | |
 |
First step is to switch off the current source | |
 |
Otherwise, move the source using a wooden stick | |
 |
Attend to the victim | |
 |
Check for breathing | |
 |
No breathing, do Cardio pulmonary resuscitation (CPR) | |
 |
Call emergency medical aid | |
 |
If breathing, do a physical examination | |
 |
Treat for minor burns | |
 |
Re-establish vital functions | |
 |
Excessive burns may require hospitalization/ surgery | |
 |
Supportive care must be provided |
Prevention
 |
Proper design, installation, maintenance of electric devices | |
 |
Educating the public regarding electrical devices | |
 |
Keep electrical gadgets out of children’s reach | |
 |
Learn to respect electricity and electrical devices |
Our Recommended Products
Obesity
Old Age